For one, exports have been robust this year. An economist at one large European lender notes his recent tour of Chinese manufacturers yielded zero complaints about currency strength. An artificial drop may also prompt other regional exporters like South Korea, Indonesia and Vietnam to make a similar move, providing little advantage. Worse, such a fall would spur greater outflows from Chinese markets.
It would also become costlier for Chinese corporates – including cash-strapped developers – to make payments on outstanding dollar obligations. Data from the Bank for International Settlements show global banks’ cross-border claims on Chinese entities totalled $526 billion at the end of 2023.
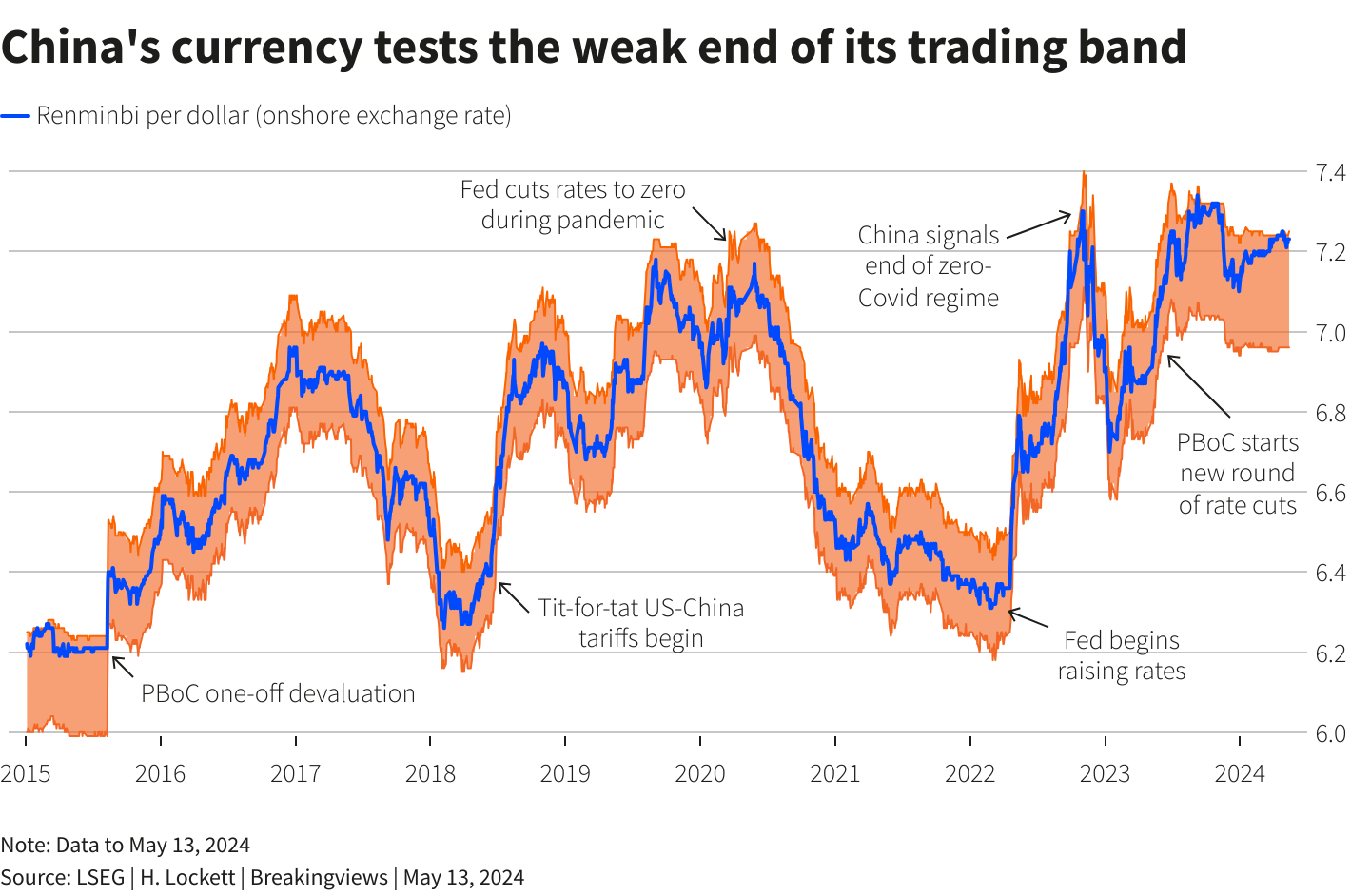
China learned the dangers of shock devaluation the hard way. In 2015, that action triggered a rout so severe the People’s Bank of China burnt through $1 trillion of foreign reserves and bolted on new capital controls to halt the fall. Today the exchange rate, which can trade 2% in either direction of a daily midpoint set by the central bank, is stuck fast against the weak side of that trading band, as the U.S. Federal Reserve’s higher-for-longer rates regime incentivises investors to shun low-yielding Chinese bonds in favor of Treasuries.
Little wonder that in January a strong currency topped President Xi Jinping’s list of priorities for making China into a “financial powerhouse”. Inflicting fresh scars on the currency’s few major foreign holders would only hurt long-term ambitions to internationalise the renminbi too.
This preference for stability could be tested in November if Donald Trump returns to the White House. The man behind the first U.S.-China trade war has threatened tariffs of 60% on Chinese goods if elected. That might be enough to naturally crater the currency.
Allowing a sharp one-off fall now risks giving away the central bank’s preferred level, potentially creating a line in the sand it would then have to defend. A long, slow grind lower better suits Beijing’s interests.
Follow @KangHexin on X
CONTEXT NEWS
The Chinese renminbi has weakened 1.9% against the U.S. dollar this year.
The onshore exchange rate on May 13 hit 7.2332 per dollar to trade 1.8% weaker than People’s Bank of China daily reference rate, which limits the transactions to 2% above or below the midpoint.
For more insights like these, click here to try Breakingviews for free.
Editing by Una Galani and Aditya Sriwatsav
Breakingviews
Reuters Breakingviews is the world’s leading source of agenda-setting financial insight. As the Reuters brand for financial commentary, we dissect the big business and economic stories as they break around the world every day. A global team of about 30 correspondents in New York, London, Hong Kong and other major cities provides expert analysis in real time.
Sign up for a free trial of our full service at https://www.breakingviews.com/trial and follow us on Twitter @Breakingviews and at www.breakingviews.com. All opinions expressed are those of the authors.


